
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee jointAt the initial stage of development, pathology manifests itself by pain in the knee, moderately expressed and emerging in motion, moving along the steps.An unpleasant symptom may appear if a person spends a lot of time standing or tries to get up after being in a sitting position for a long time.At rest, health generally improves.Intense intense intense pain spontaneously occurs.Most patients previously had prolonged discomfort during physical activity and when walking. In this case, growing pain may be the main sign of the development of gonarthrosis.The disease is developing gradually, for several months or several years, when it is not yet visible, deformation and intense pain. But during this period, discomfort in the knees, which occurs from time to time. Remember that the earlier you see a doctor, the easier the treatment will be and successfully.Do not delay a visit to a specialist, pending irreversible consequences. Take measures as soon as you notice the symptoms of the disease.The obvious signs of osteoarthritis of the knee joint begin to manifest itself as the structure of the cartilage shells, a decrease in the production of synovial fluid and damage to the joint bag. At the initial stage of increasing pathological changes, as a rule, there are no pronounced symptoms, but at the same time, a slight stiffness can be present in the morning.When pronounced symptoms and various symptoms appear, osteoarthritis, as a rule, is already in the late stage of their development. Currently, there are already serious damage to the structures of the knee joint, so that the disease enters the acute phase. The manifestations characteristic of the acute period of development of osteoarthritis include:increased pain;Change of approach;lameness;Crunch while moving;Swelling of soft tissues;an increase in the knee due to the accumulation of liquid;Limit mobility in the joint.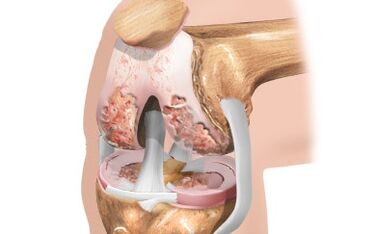
When knee osteoarthritis develops, symptoms can grow long enough, but when the disease is going to the last stages of manifestation of a joint disorder, the quality of life considerably reduces quality of life.The synovial shell in the context of damage to joint surfaces begins to be ignited, which leads to a violation of the mobility of the entire joint. Any movement with a damaged joint can be very painful.At palpation, a significant increase in local body temperature is noted.As a rule, the effective treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint with conservative methods is only possible at the beginning of the development of the disease.Thus, when the signs of the disease appear, consult a doctor for consultation.In the development of a condition such as knee osteoarthritis, symptoms and treatment are interconnected, because if the first stages of the development of the disease, joint surfaces can always be completely restored and improved by local metabolism, then in subsequent stages, the drug treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint may often not have a positive effect, becausethat bone structures are exposed.The 1st degree osteoarthritis takes place almost without visible symptoms. This development phase is characterized by:fatigue in the legs;A slight decrease in mobility, which is generally observed immediately after sleep.Symptoms of pain, if and occur, manifest themselves in a slight degree. At the moment, knee osteoarthritis resembles the X -ray in the form of small bumps on the cartilage fabric and the surface of the bones.With osteoarthritis of the 2nd degree knee joint, the symptoms are more pronounced. The pain is already resulting from the minimum load or immediately afterwards. In the affected part of the leg, the pain is caused by almost all movements. After a fairly long rest, it usually goes completely. However, the next physical actions immediately cause pain. About the second stage in the development of the disease, pain sensations are added:Crunch in the knee joint during movements;A reduced opportunity to build the leg normally on the knee;Change of joint bones;Progressive synovitis.A crunchy raw arthosis of the joints, as a rule, is first barely audible, but with the course of the disease, it becomes very strong and distinct. When you try to fold the leg into the knee, acute pain occurs. In some cases, this is only possible in a corner of 90 degrees, then with difficulty and overcome the pain. The change in the form of the articulation also becomes obvious, which is also aggravated by the accumulation of pathological fluid.
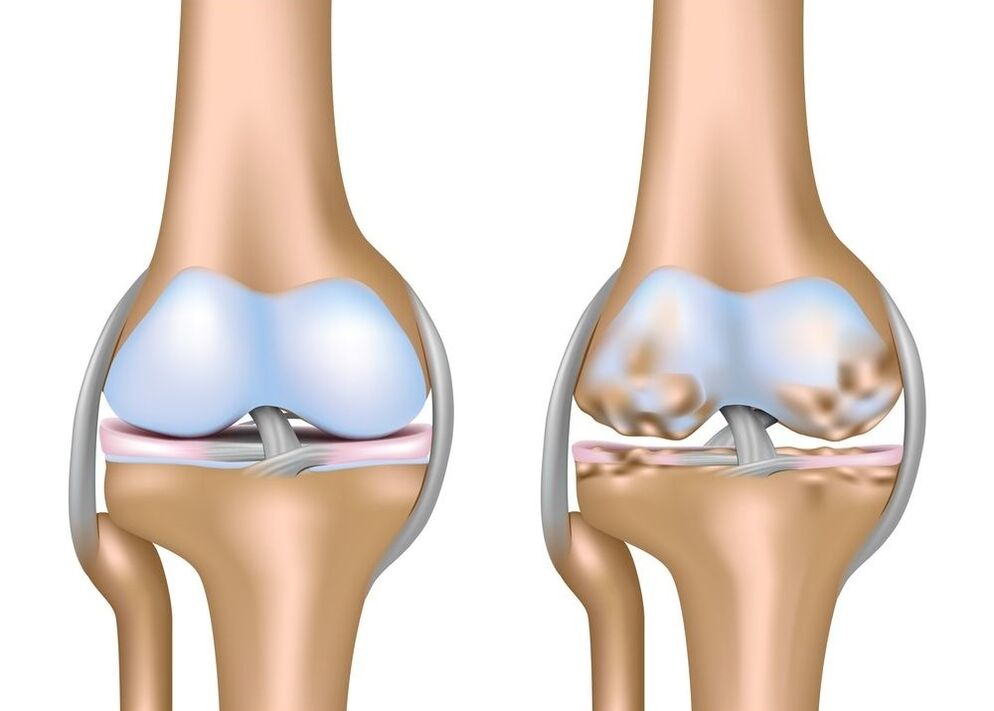
The characteristics of the 3rd degree of osteoarthritis are intense pain which is independent of the quantity, the intensity of physical activity. The articulation disturbs a person even at night, this causes significant drawbacks.X -ray can show global changes in cartilage, articular surface, non -characteristic growth. The o or X -shaped curvature leads a person to disability. These are the consequences that the cartilage fabric has already exhausted and that the bone tissue has entered the "movement".Gonarthrosis is a disease of a dystrophic degenerative nature, in which the destruction of the cartilage occurs and the joint is distorted. The signs of the disease are intense pain, a deformation of the limbs, an unequal distribution of the load on the bone muscle system, the development of complications and a significant decrease in mobility to the invalidity of the patient.





















